The Computer Tutor
Additional Information about the Motherboard
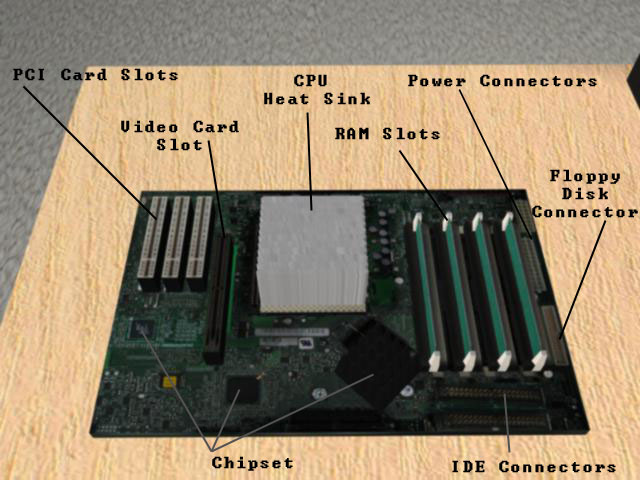
The only time that you would usually replace your motherboard is if you have a home-built computer or are planning on building your own computer. Most motherboards on pre-built computers are designed and mounted in the case in such a way that they are impossible to replace on your own. However, if you do want to try building your own computer, there are a few things you need to know about the motherboard.
What it supports
Whenever you replace a motherboard, youa re most likely replacing the CPU and the RAM as well. There are several different types of CPUs and several different types of RAM that a motherboard can support, so you have to know what CPU and what type of RAM you have or are going to get before you purchase a motherboard.
The chipset
A motherboard's chipset defines everything about it, from the type and speed of CPU and the type of RAM that it will support, to the number of graphics and PCI cards it can support, to the number of extras such as integrated sound, network connectors, and USB ports are included on the board.
Integrated extras
Some motherboards come with integrated graphics and sound cards, so if you don't plan on using an external graphics card to play 3D games or run graphics software, or if you don't need a separate sound card for recording or mixing sound, you can save a lot of money by getting a motherboard with these integrated options. It is usually best to make sure that they can support external graphics or sound cards if necessary, though, in case your computer needs change over time and you need external cards in the future.
RAID storage option
If you plan on having several hard drives in your computer, you may want to consider getting a motherboard that supports RAID. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks, and it is a technology that divides the data stored and accessed on your hard drives evenly between several hard drives. This allows your computer to see multiple hard drives as just one storage space, which makes it easier to manage file systems over multiple drives. It also allows for redundancy in the data stored: since the data is written evenly between the two disks, only a part of any given string of data will be stored on each hard drive. Thus, if one drive goes out, the data on it isn't lost – when a new hard drive is placed into the RAID, the computer will reconstruct the lost data from the data stored on the other disks. While placing hard drives in a RAID reduces their overall capacity, if you plan on having large hard drives with a lot of storage space installed in your computer, it may be best to sacrifice a bit of storage space for the security and redundancy of a RAID.
Necessary external connections
The greatest variation in motherboards comes from the number and type of external connectors that come pre-installed. Ethernet ports, USB, Firewire, PS/2, serial, and parallel ports are standard on most motherboards, but the number and configuration of the ports may vary. If you are planning on building a completely modern computer, you can get motherboards with no support for PS/2, serial, or parallel ports, as these standards are rarely used in modern accessories, but you should always be aware of what you are planning to interface with your computer before choosing to leave any options out of your motherboard purchase.
Now that you know all about the motherboard, you can check out: