The Computer Tutor
The Sound Card
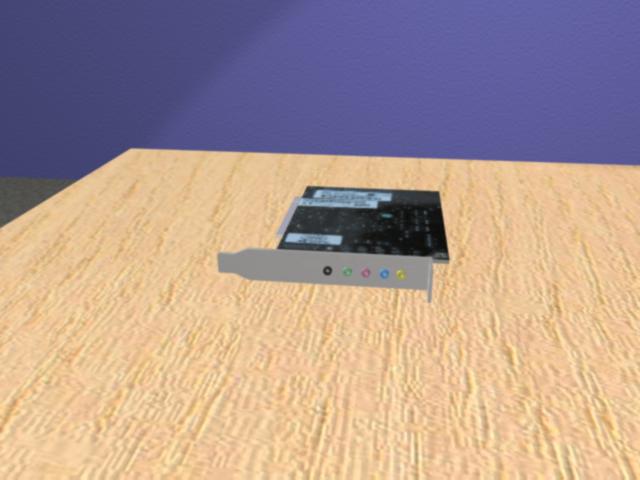

The sound card on your computer exists to take sound in a digital format from music and video files and convert it to an analog format that is output through speakers and headphones at frequencies that we are able to hear. They are also capable of doing the reverse – taking in analog sound through a microphone and converting it to a digital format so that it can be compressed and used in audio mixing or video production. Some computers may not even have external sound cards like the one shown here – rather, they have a very basic sound card built straight onto the motherboard. If your speaker connects to a port near the PCI slots on the back of your computer, and if it is in a long row with many other colored plugs, then you probably have an external sound card. If you have a smaller row of audio plugs located near your USB ports or your ethernet connection, then you probably have a built-in sound card.
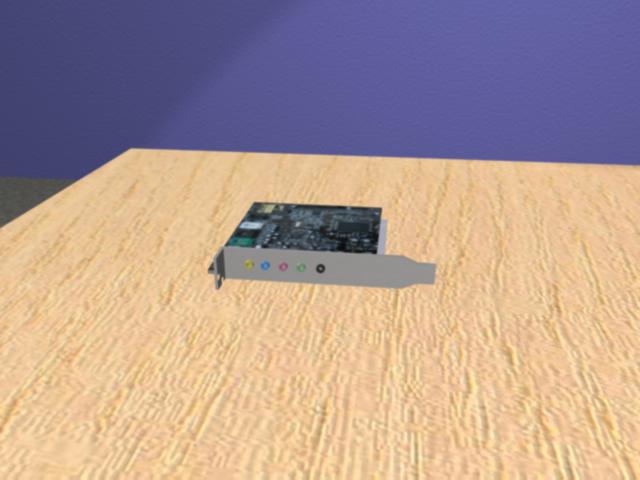
Like the video card, the sound card in a standard computer is usually something that the average user does not need to concern themselves much with. However, if you are an audiophile or you do a lot of sound recording and sound mixing on your computer, you may want to look into the specifications of your sound card and upgrade if you do not feel that it is giving you the audio quality you desire.
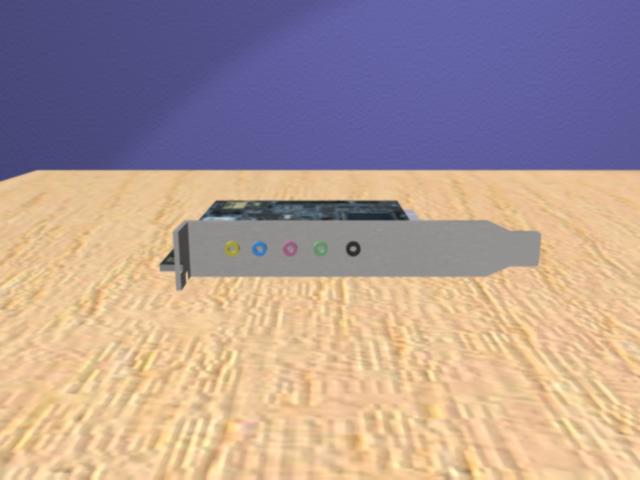

The sound card seen here has five audio ports, each of which corresponds to a different method of input or output. The green port is where you connect your computer's speakers, your headphones, front speakers if you have surround sound, or any other device through which sound can be output. The pink port is where you would connect an external microphone in order to record sound to the computer. The blue port is an analog line-in, where you can connect an audio plug from another source, such as your TV, in order to input the sound from that device into your computer. The yellow (or orange) port is for a subwoofer, if your speaker system has one, or for the center speaker if you have surround sound, and the black port is for rear speakers if you have surround sound. Though some sound card colors may differ, the pink and green ports are always for sound input and output respectively, and there is almost always an analog line-in as the third plug, though it may be blue or black depending on whether your computer supports surround sound and has five plugs, or whether it only has three.
Some sound cards may also have a rectangular orange plug that looks like a monitor port. That is a MIDI device connector, for connecting a joystick or MIDI device, such as a MIDI keyboard, to your computer. These are holdover ports from the 90s, when MIDI devices were popular, but most of this port's functionality has been phased out in more advanced sound cards.
Now that you have familiarized yourself with the computer's sound card, you can check out: